- Standalone Applications
- ChemCurator
- Compliance Checker
- Compound Registration
- Quick Start Guide
- Compound Registration User's Guide
- Overview
- Compound Registration Abbreviations
- Definitions of Terms
- Compound Registration Introduction
- Login
- Dashboard page
- Autoregistration
- Bulk Upload
- Advanced Registration
- Search
- User Profile
- Download
- Browse page
- Appendix A. Calculations
- Appendix B. Markush Structures
- Multi-Component compounds
- Restricted compounds
- Configuration Guide
- Deployment Guide
- Compound Registration FAQ
- Compound Registration System Requirements
- Compound Registration History of Changes
- API documentation
- Instant JChem
- Instant Jchem User Guide
- Getting Started
- IJC Projects
- IJC Schemas
- Viewing and Managing Data
- Lists and Queries
- Collaboration
- Import and Export
- Editing Databases
- Relational Data
- Chemical Calculations and Predictions
- Chemistry Functions
- Security
- Scripting
- Updating Instant JChem
- Tips and Tricks
- Instant JChem Tutorials
- Building a relational form from scratch
- Building more complex relational data models
- Defining a security policy
- Filtering items using roles
- Lists and Queries management
- Query building tutorial
- Reaction enumeration analysis and visualization
- SD file import basic visualization and overlap analysis
- Using Import map and merge
- Using Standardizer to your advantage
- Pivoting tutorial
- Instant JChem Administrator Guide
- Admin Tool
- IJC Deployment Guide
- Supported databases
- JChem Cartridge
- Using Oracle Text in Instant JChem
- Deployment via Java Web Start
- Startup Options
- Shared project configuration
- Accessing data with URLs
- Instant JChem Meta Data Tables
- Test to Production Metadata Migrator
- Filtering Items
- Deploying the IJC OData extension into Spotfire
- Reporting a Problem
- Manual Instant JChem schema admin functions
- SQL Scripts for Manual Schema Upgrade
- Database Row Level Security
- JccWithIJC
- Deploying Spotfire Middle Tier solution
- Instant JChem Developer Guide
- Working With IJC Architecture
- IJC API
- Groovy Scripting
- Good Practices
- Schema and DataTree Scripts
- Simple SDF Exporter
- Relational SDF Exporter
- CDX File Importer
- Data Merger or Inserter from an SDF file
- Markush DCR Structures Exporter
- Select Representative Member of Clusters
- Table Standardizer
- Populate a Table with Microspecies
- Create a Diverse Subset
- Pearson Linear Correlation Co-efficient Calculator
- PDF Trawler
- Simple Substructure Search
- Intersecting Sets
- Find Entries with Duplicated Field Value
- Importing Multiple SDF Files
- Calling External Tools
- Create Relational Data Tree
- Forms Model Scripts
- Button Scripts
- Execute Permanent Query
- Patent Fetcher Button
- Batch Searching Button
- Import or Export a Saved Query SDF Button
- Back and Next Buttons
- Add Annotations Button
- Simple Structure Checker Button
- Advanced Structure Checker Button
- Calculate MolWeight and generate SMILES
- Get Current User
- Simple ChemicalTerms evaluator
- Edit Molecule Button
- TanimotoSimilarityButton
- TanimotoMultiple
- Execute Permanent Query Based On Its Name
- Open existing view in the same dataTree
- Export selection to file
- Generate random resultset from actual resultset
- Form Scripts
- Groovy Scriptlets
- Buttons vs Scripts
- Creating New Entities
- Creating New Fields
- Reading Molecules From a File
- Insert or Update a Row
- Evaluator
- Create or Find a Relationship
- Adding an Edge to a Data Tree
- Exporting Data to a File
- Connect to an External Database
- Create a New ChemTerm Field
- Create a New Dynamic URL Field
- Create a New Static URL Field
- Java Plugins
- Instant JChem FAQ
- Instant JChem Installation and Upgrade
- New Features
- New Features in IJC Q3 2019
- New Features in IJC Q2 2019
- New Features in IJC Q1 2019
- New Features in IJC Q4 2018
- New Features in IJC Q3 2018
- New Features in IJC Q2 2018
- New Features in IJC Q1 2018
- New Features in IJC Q4 2017
- New Features in IJC Q3 2017
- New Features in IJC Q2 2017
- New Features in IJC Q1 2017
- New Features in IJC Q4 2016
- New Features in IJC Q3 2016
- New Features in IJC Q2 2016
- New Features in IJC Q1 2016
- New Features in IJC Q4 2015
- New Features in IJC Q3 2015
- New Features in IJC Q2 2015
- New Features in IJC Q1 2015
- New Features in IJC 14.7.7
- New Features in IJC Q4 2019
- Instant JChem Licensing
- IJC Getting Help and Support
- Instant JChem System Requirements
- Instant JChem History of Changes
- Instant Jchem User Guide
- Markush Editor
- Marvin Live
- Marvin Live user guide
- Marvin Live history of changes
- Marvin Live install guide
- Marvin Live - cloud deployment
- Marvin Live developer guide - sending data
- Marvin Live developer guide - resolver plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - real time plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - export plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - theme customization
- Marvin Live migration guide
- Marvin Live developer guide - storage plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - real time plugin templates
- Marvin Live configuration guide
- MarvinSketch
- Introduction to MarvinSketch
- MarvinSketch User's Guide
- MarvinSketch Getting Started
- MarvinSketch Graphical User Interface
- Canvas in MarvinSketch
- Menus of MarvinSketch
- Toolbars of MarvinSketch
- Pop-up Menus of MarvinSketch
- Status bar of MarvinSketch
- Dialogs of MarvinSketch
- Shortcuts in MarvinSketch
- Customizing MarvinSketch GUI
- Configurations of MarvinSketch
- Services module
- Working in MarvinSketch
- Structure Display Options
- Basic Editing
- Drawing Simple Structures
- Drawing More Complex Structures
- Substructure Groups in MarvinSketch
- Draw R-groups in MarvinSketch
- Draw link nodes
- Homology Groups in MarvinSketch
- Atom lists and NOT lists
- Position variation in MarvinSketch
- Markush structures in MarvinSketch
- How to draw query structures
- Biomolecules
- Atom, bond and molecule properties
- Drawing reactions
- Use integrated calculations in Marvin
- Graphical objects
- Import and export options
- Multipage documents
- Printing in MarvinSketch
- Chemical Features in MarvinSketch
- Marvin OLE User's Guide
- Appendix for MarvinSketch
- Tutorials
- Additional information
- MarvinSketch Developer's Guide
- MarvinSketch Application Options
- MarvinSketch Installation and Upgrade
- MarvinSketch Licensing
- MarvinSketch Getting Help and Support
- MarvinSketch Downloads
- MarvinSketch History of Changes
- MarvinView
- Introduction to MarvinView
- MarvinView Developer's Guide
- MarvinView Application Options
- MarvinView Installation and Upgrade
- MarvinView User's Guide
- MarvinView Getting started
- How to Use MarvinView Features
- MarvinView Graphical User Interface
- MarvinView Licensing
- MarvinView Getting Help and Support
- MarvinView Downloads
- MarvinView History of changes
- Molconvert
- Plexus Suite
- Quick Start Guide - Plexus Suite
- Plexus Suite User Guide
- Log in to Plexus Suite
- The Plexus Suite Dashboard
- Importing New Data
- Exporting Your Data
- Browsing in Your Data Set
- Selecting Data
- Searching in Your Database
- Saved Queries
- List Management
- Sorting Data
- Sharing Data with Other Users
- Calculating Molecular Properties for Single Compounds
- Adding calculated columns to tables
- Scaffold Based Enumeration
- Reaction Based Enumeration
- Registering Molecules in the Corporate Database
- ChemAxon Assay
- Charts view
- Plexus Suite Video Tutorials
- Plexus Suite Administrator Guide
- Plexus Connect Authentication
- Sharing Schema Items Among Users
- Business Flags
- Row-level Security
- Building blocks
- Admin Tools
- Adding JavaScript Files for Custom Functionality
- Writing JavaScript Files for Custom Functionality
- Integration with ChemAxon's Compound Registration System
- Shared data sources in Plexus Connect
- Configuration Files
- Edit Views
- Simple table
- Installation and System Requirements of Plexus Suite
- Plexus Suite Licensing
- Getting Help and Support for Plexus Suite
- Plexus Suite FAQ
- Plexus Suite Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use for the Plexus Suite Demo Site
- Plexus Suite History of Changes
- Schema Refresh Without Restart
- Zosimos
- Toolkits and Components
- AutoMapper
- Calculator Plugins
- Introduction to Calculator Plugins
- Calculator Plugins User's Guide
- Calculator Plugins Developer's Guide
- Background materials
- Calculation of partial charge distribution
- Generate3D
- Isoelectric point (pI) calculation
- LogP and logD calculations
- NMR model prediction
- pKa calculation
- Red and blue representation of pKa values
- Tautomerization and tautomers
- Validation results
- Tautomerization and tautomer models of ChemAxon
- Theory of aqueous solubility prediction
- The tautomerization models behind the JChem tautomer search
- Calculator Plugins Licensing
- Calculator Plugins FAQ
- Calculator Plugins Getting Help and Support
- Calculator Plugins History of Changes
- Calculator Plugins System Requirements
- Biomolecule Toolkit
- ChemAxon Synergy
- Document to Structure
- JChem Base
- JChem Base Administration
- JChem Base Developer's Guide
- JChem Base User's Guide
- Query Guide
- Search types
- Similarity search
- Query features JCB
- Stereochemistry JCB
- Special search types
- Search options
- Tautomer search - Vague bond search - sp-Hybridization
- Search Options Guide
- Atomproperty specific search options
- Attached data specific search options
- Bond specific search options
- Chemical terms specific search options
- Database specific search options
- General search options
- Hitdisplay specific search options
- Markush structure specific search options
- Performance specific search options
- Polymer specific search options
- Query feature specific search options
- Reaction specific search options
- Resultset specific search options
- Similarity specific search options
- Stereo specific search options
- Tautomer specific search options
- Standardization JCB
- Hit display-coloring
- Appendix JCB
- Matching Query - Target Examples
- jcsearch Command Line Tool
- jcunique Command Line Tool
- Homology Groups and Markush Structures
- Query Guide
- JChem Base FAQ
- JChem Base History of Changes
- JChem Base Getting Help and Support
- JChem Base Licensing
- JChem Choral
- JChem Neo4j Cartridge
- JChem Oracle Cartridge
- JChem Microservices
- JChem PostgreSQL Cartridge
- JChem Web Services Classic
- JKlustor
- Markush Tools
- Marvin JS
- Getting Started with Marvin JS
- Marvin JS Installation and System Requirements
- Marvin JS Developer's Guide
- Marvin JS User's Guide
- Editor Overview
- Editor Canvas
- Dialogs
- Abbreviated groups dialog
- Atom query properties dialog
- Attached Data dialog
- Bond properties dialog
- Export dialog
- Import dialog
- Periodic table dialog
- Atom properties dialog in Marvin JS
- Pseudo atom dialog
- Reaxys Group Generics dialog
- Repeating group dialog
- R-group dialog
- R-logic dialog
- Set box color dialog
- Text dialog
- View Settings dialog
- Toolbars
- Context menus
- Drawing and editing options
- Feature overview pages
- Keyboard Shortcuts in Marvin JS
- Editor Overview
- Marvin JS API Reference
- Online Examples
- Marvin JS Licensing
- Marvin JS History of Changes
- Marvin JS FAQ
- Marvin JS Getting Help and Support
- Marvin JS Video Tutorials
- Name to Structure
- Reactor
- Reactor User's Guide
- Introduction to Reactor
- Reactor Getting Started
- Reactor Concepts
- Reactor Examples
- Working with Reactor
- Specifying Reactions
- Specifying Reactants
- Reaction Mapping
- Reaction Rules
- Reactant Combinations
- Running Reactor
- Reactor Interfaces
- Reactor Application
- Reactor Command-line Application
- Reactor in Instant JChem
- Reactor in JChem for Excel
- Reactor in KNIME
- Reactor in Pipeline Pilot
- Reactor in Plexus Suite
- API, Web Services
- Glossary
- Reactor FAQ
- Reactor Licensing
- Reactor Getting Help and Support
- Reactor History of Changes
- Reactor Configuration Files
- Reactor User's Guide
- Screen
- Standardizer
- Standardizer User's Guide
- Standardizer Introduction
- Standardizer Getting Started
- Standardizer Concepts
- Working with Standardizer
- Standardizer Actions
- Add Explicit Hydrogens
- Alias to Atom
- Alias to Group
- Aromatize
- Clean 2D
- Clean 3D
- Clear Isotopes
- Clear Stereo
- Contract S-groups
- Convert Double Bonds
- Convert Pi-metal Bonds
- Convert to Enhanced Stereo
- Create Group
- Dearomatize
- Disconnect Metal Atoms
- Expand S-groups
- Expand Stoichiometry
- Map
- Map Reaction
- Mesomerize
- Neutralize
- Remove Absolute Stereo
- Remove Atom Values
- Remove Attached Data
- Remove Explicit Hydrogens
- Remove Fragment
- Remove R-group Definitions
- Remove Stereo Care Box
- Replace Atoms
- Set Absolute Stereo
- Set Hydrogen Isotope Symbol
- Strip Salts
- Tautomerize
- Transform
- Ungroup S-groups
- Unmap
- Wedge Clean
- Remove
- Standardizer Transform
- Custom Standardizer Actions
- Remove Solvents
- Creating a Configuration Standardizer
- Interfaces Standardizer
- Standardizer Actions
- Standardizer Developer's Guide
- Standardizer Installation and System Requirements
- Standardizer Licensing
- Standardizer Getting Help and Support
- Standardizer History of Changes
- Standardizer User's Guide
- Structure Checker
- Structure Checker User's Guide
- Introduction
- Structure Checker Getting Started
- Structure Checker Concepts
- Working with Structure Checker
- Checker List
- Abbreviated Group StrCh
- Absent Chiral Flag
- Absolute Stereo Configuration
- Alias
- Aromaticity Error
- Atom Map
- Atom Query Property
- Atom Value
- Atropisomer
- Attached Data StrCh
- Bond Angle
- Bond Length
- Brackets
- Chiral Flag
- Chiral Flag Error
- Circular R-group Reference
- Coordination System Error
- Covalent Counterion
- Crossed Double Bond
- Custom Checkers and Fixers
- Double Bond Stereo Error
- EZ Double Bond
- Empty Structure
- Explicit Hydrogen
- Explicit Lone Pairs
- Incorrect Tetrahedral Stereo
- Isotope
- Metallocene Error
- Missing Atom Map
- Missing R-group Reference
- Molecule Charge
- Multicenter
- Multicomponent
- Multiple Stereocenter
- Non-standard Wedge Scheme
- Non-stereo Wedge Bond
- OCR Error
- Overlapping Atoms
- Overlapping Bonds
- Pseudo Atom
- Query Atom
- Query Bond
- Racemate
- Radical
- Rare Element
- R-atom
- Reacting Center Bond Mark
- Reaction Map Error
- Relative Stereo
- R-group Attachment Error
- R-group Bridge Error
- R-group Reference Error
- Ring Strain Error
- Solvent
- Star Atom
- Stereo Care Box
- Stereo Inversion Retention Mark
- Straight Double Bond
- Substructure
- Three Dimension 3D
- Unbalanced Reaction
- Unused R-group Reference
- Valence Error
- Valence Property
- Wedge Error
- Wiggly Bond
- Wiggly Double Bond
- Creating a Configuration StrCh
- Interfaces StrCh
- Checker List
- Structure Checker Developer's Guide
- Structure Checker Installation and System Requirements
- Structure Checker Licensing
- Structure Checker Getting Help and Support
- Structure Checker History of Changes
- Structure Checker User's Guide
- Structure to Name
- Third-party Integration
- Cross Product Documentation
- ChemAxon Configuration Folder
- Chemical Fingerprints
- Chemical Terms
- File Formats
- Basic export options
- Compression and Encoding
- Document formats
- Graphics Formats
- Molecule file conversion with Molconverter
- Molecule Formats
- CML
- MDL MOL files
- Daylight SMILES related formats
- ChemAxon SMILES extensions
- IUPAC InChI, InChIKey, RInChI and RInChIKey
- Name
- Sequences - peptide, DNA, RNA
- FASTA file format
- Protein Data Bank (PDB) file format
- Tripos SYBYL MOL and MOL2 formats
- XYZ format
- Gaussian related file formats
- Markush DARC format - VMN
- CSV
- Input and Output System
- License Management
- Long Term Supported Releases - LTS
- Notice about CAS Registry Numbers®
- Other versions
- Public Repository
- Scientific Background
- Structure Representation
- Structure Representation - Class Representation
- Aromaticity
- Implicit, Explicit and Query Hydrogens
- Assigning stereochemistry descriptors
- Cleaning options
- Deprecated and Removed Methods
- Relative configuration of tetrahedral stereo centers
- Iterator Factory
- Atom and bond-set handling
- Graphic object handling
- Supported Java Versions
- Legal
- Discontinued Products
- Document to Database
- Fragmenter
- MarvinSpace
- MarvinSpace User's Guide
- MarvinSpace Developer's Guide
- MarvinSpace History of Changes
- Metabolizer
Training the logP Plugin
This manual gives you a walk-through on how to train the log P Plugin:
Introduction
If you think your experimental data could improve the performance of the default log P calculator, you can take advantage of the supervised log P learning method that is built into the logP calculator.
If you create a local log P model, the scope of the log P calculator will be limited. It means that the calculated log P will only provide reasonable prediction for a few types of structures. Practically only those types of structures will be predicted correctly which were introduced to the training set during the teaching process. For example, if the training set contains only certain types of hydrocarbon but no other functional groups are present in the training set, the predicted log P of any amine-like molecule will not be accurate.
Therefore you need to be aware that a more robust general log P model requires a large, diverse training set with thousands of structures. You can generate a log P training library with the cxtrain command line tool.
Training steps
Preparing the input file
As the first step of the training you have to create a training set from your experimental data. The training set should have a format which supports saving molecular properties (SDF or MRV). This can be easily done by using the graphical user interface of Instant JChem. This training set must contain the following items:
-
structure
-
logP values in a property field named LOGP
See the following bit of an example file as an example (logP_trainingset.sdf):
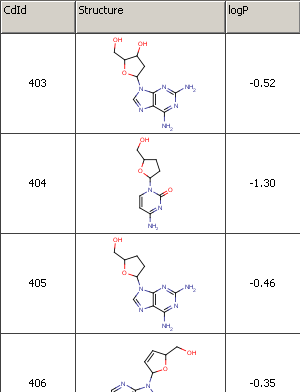
Fig. 1 Example file used for training
Creating the training library
Then you have to run the training algorithm which creates a log P training library from your pre-compiled set. Execute the following command from command line:
cxtrain logp -t LOGP -i [library name] -a [training file] Example
cxtrain logp -t LOGP -i mylogp -a logP_trainingset.sdf The created log P training library mylogp can be used via marvinsketch, cxcalc, or chemicalterms.
Applying the training library
MarvinSketch
To apply the pre-generated training library mylogp in MarvinSketch, do the following steps:
-
Choose MarvinSketch menu Tools > Partitioning > logP .
-
Select the User defined method to activate the training option.
-
If you have created multiple training sets, choose one from the dropdown list below the checkbox.
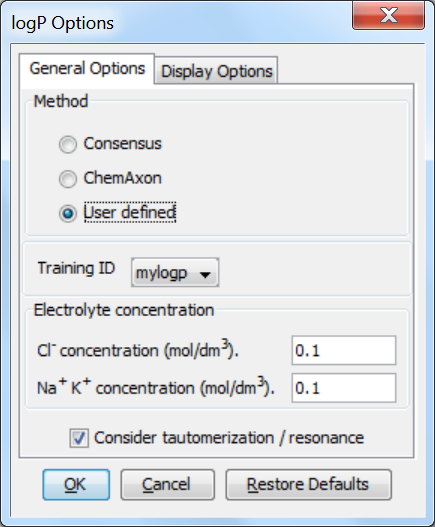
Fig. 2 The log P options window showing how to apply the training library
Cxcalc
To apply your log P dataset use the --trainingid and the --method parameter:
cxcalc logp `--method user --trainingid `[library name] [input file/string]
Example
cxcalc logp --method user --trainingid mylogp "CC(C)CCO"Result
id logP1 1,13
Without training the result is:
id logP1 1,09
Chemical Terms
Chemical Terms are available from Chemical Terms Evaluator or from Instant JChem. The method and trainingid parameters can be used in Chemical Terms Evaluator as well:
evaluate -e "logp('method:user trainingid:[library name]')" "[input file/string]"
Example
evaluate -e "logp('method:user trainingid:mylogp')" "CC(C)CCO" Instant JChem
You can also apply your log P training library via Chemical Terms in Instant JChem.
-
Choose the 'New Chemical Terms Field icon' on the panel on the right side.
-
Type the chemical term into the window, use the parameters method and trainingid. Do not forget to adjust the Name, the Type and the DB Column Name.
Example
The following figure presents the usage of log P training in the 'New Chemical terms' window. The expression
logP('method:user trainingid:mylogp')
defines that the plugin use the user defined log P training library myplogp .
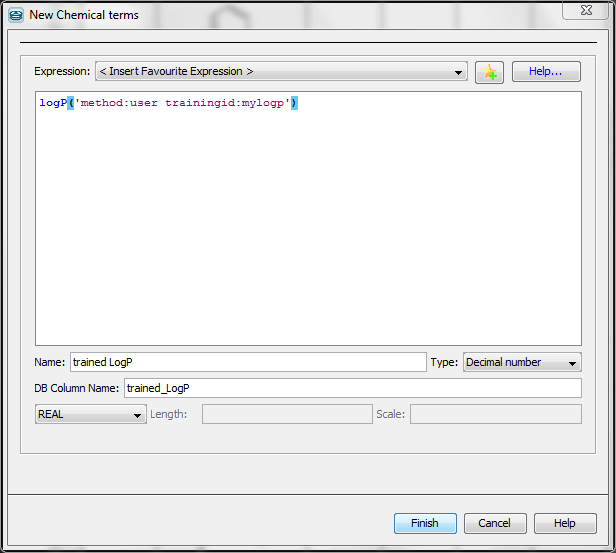
Fig. 3 Using Chemical Terms function for training in Instant JChem
Part of the results of this calculation is presented below. You can see the difference between the untrained (column LogP ) and trained (column trained LogP ) values.
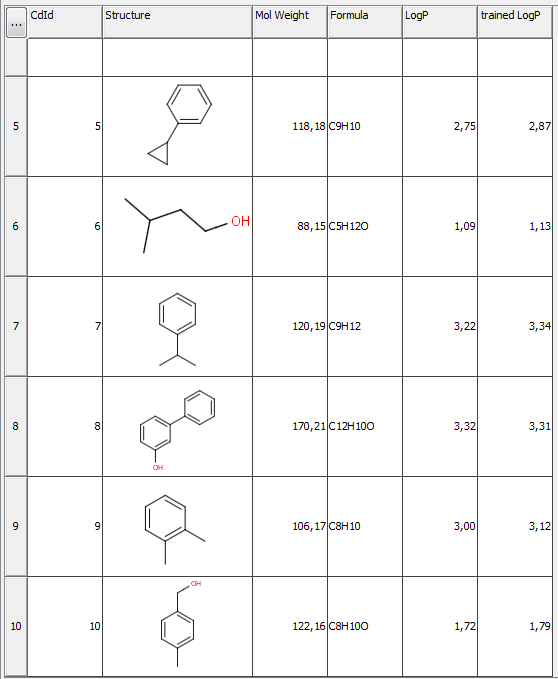
Fig. 4 JChem table showing the untrained and trained log P values