- Standalone Applications
- ChemCurator
- Compliance Checker
- Compound Registration
- Quick Start Guide
- Compound Registration User's Guide
- Overview
- Compound Registration Abbreviations
- Definitions of Terms
- Compound Registration Introduction
- Login
- Dashboard page
- Autoregistration
- Bulk Upload
- Advanced Registration
- Search
- User Profile
- Download
- Browse page
- Appendix A. Calculations
- Appendix B. Markush Structures
- Multi-Component compounds
- Restricted compounds
- Configuration Guide
- Deployment Guide
- Compound Registration FAQ
- Compound Registration System Requirements
- Compound Registration History of Changes
- API documentation
- Instant JChem
- Instant Jchem User Guide
- Getting Started
- IJC Projects
- IJC Schemas
- Viewing and Managing Data
- Lists and Queries
- Collaboration
- Import and Export
- Editing Databases
- Relational Data
- Chemical Calculations and Predictions
- Chemistry Functions
- Security
- Scripting
- Updating Instant JChem
- Tips and Tricks
- Instant JChem Tutorials
- Building a relational form from scratch
- Building more complex relational data models
- Defining a security policy
- Filtering items using roles
- Lists and Queries management
- Query building tutorial
- Reaction enumeration analysis and visualization
- SD file import basic visualization and overlap analysis
- Using Import map and merge
- Using Standardizer to your advantage
- Pivoting tutorial
- Instant JChem Administrator Guide
- Admin Tool
- IJC Deployment Guide
- Supported databases
- JChem Cartridge
- Using Oracle Text in Instant JChem
- Deployment via Java Web Start
- Startup Options
- Shared project configuration
- Accessing data with URLs
- Instant JChem Meta Data Tables
- Test to Production Metadata Migrator
- Filtering Items
- Deploying the IJC OData extension into Spotfire
- Reporting a Problem
- Manual Instant JChem schema admin functions
- SQL Scripts for Manual Schema Upgrade
- Database Row Level Security
- JccWithIJC
- Deploying Spotfire Middle Tier solution
- Instant JChem Developer Guide
- Working With IJC Architecture
- IJC API
- Groovy Scripting
- Good Practices
- Schema and DataTree Scripts
- Simple SDF Exporter
- Relational SDF Exporter
- CDX File Importer
- Data Merger or Inserter from an SDF file
- Markush DCR Structures Exporter
- Select Representative Member of Clusters
- Table Standardizer
- Populate a Table with Microspecies
- Create a Diverse Subset
- Pearson Linear Correlation Co-efficient Calculator
- PDF Trawler
- Simple Substructure Search
- Intersecting Sets
- Find Entries with Duplicated Field Value
- Importing Multiple SDF Files
- Calling External Tools
- Create Relational Data Tree
- Forms Model Scripts
- Button Scripts
- Execute Permanent Query
- Patent Fetcher Button
- Batch Searching Button
- Import or Export a Saved Query SDF Button
- Back and Next Buttons
- Add Annotations Button
- Simple Structure Checker Button
- Advanced Structure Checker Button
- Calculate MolWeight and generate SMILES
- Get Current User
- Simple ChemicalTerms evaluator
- Edit Molecule Button
- TanimotoSimilarityButton
- TanimotoMultiple
- Execute Permanent Query Based On Its Name
- Open existing view in the same dataTree
- Export selection to file
- Generate random resultset from actual resultset
- Form Scripts
- Groovy Scriptlets
- Buttons vs Scripts
- Creating New Entities
- Creating New Fields
- Reading Molecules From a File
- Insert or Update a Row
- Evaluator
- Create or Find a Relationship
- Adding an Edge to a Data Tree
- Exporting Data to a File
- Connect to an External Database
- Create a New ChemTerm Field
- Create a New Dynamic URL Field
- Create a New Static URL Field
- Java Plugins
- Instant JChem FAQ
- Instant JChem Installation and Upgrade
- New Features
- New Features in IJC Q3 2019
- New Features in IJC Q2 2019
- New Features in IJC Q1 2019
- New Features in IJC Q4 2018
- New Features in IJC Q3 2018
- New Features in IJC Q2 2018
- New Features in IJC Q1 2018
- New Features in IJC Q4 2017
- New Features in IJC Q3 2017
- New Features in IJC Q2 2017
- New Features in IJC Q1 2017
- New Features in IJC Q4 2016
- New Features in IJC Q3 2016
- New Features in IJC Q2 2016
- New Features in IJC Q1 2016
- New Features in IJC Q4 2015
- New Features in IJC Q3 2015
- New Features in IJC Q2 2015
- New Features in IJC Q1 2015
- New Features in IJC 14.7.7
- New Features in IJC Q4 2019
- Instant JChem Licensing
- IJC Getting Help and Support
- Instant JChem System Requirements
- Instant JChem History of Changes
- Instant Jchem User Guide
- Markush Editor
- Marvin Live
- Marvin Live user guide
- Marvin Live history of changes
- Marvin Live install guide
- Marvin Live - cloud deployment
- Marvin Live developer guide - sending data
- Marvin Live developer guide - resolver plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - real time plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - export plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - theme customization
- Marvin Live migration guide
- Marvin Live developer guide - storage plugins
- Marvin Live developer guide - real time plugin templates
- Marvin Live configuration guide
- MarvinSketch
- Introduction to MarvinSketch
- MarvinSketch User's Guide
- MarvinSketch Getting Started
- MarvinSketch Graphical User Interface
- Canvas in MarvinSketch
- Menus of MarvinSketch
- Toolbars of MarvinSketch
- Pop-up Menus of MarvinSketch
- Status bar of MarvinSketch
- Dialogs of MarvinSketch
- Shortcuts in MarvinSketch
- Customizing MarvinSketch GUI
- Configurations of MarvinSketch
- Services module
- Working in MarvinSketch
- Structure Display Options
- Basic Editing
- Drawing Simple Structures
- Drawing More Complex Structures
- Substructure Groups in MarvinSketch
- Draw R-groups in MarvinSketch
- Draw link nodes
- Homology Groups in MarvinSketch
- Atom lists and NOT lists
- Position variation in MarvinSketch
- Markush structures in MarvinSketch
- How to draw query structures
- Biomolecules
- Atom, bond and molecule properties
- Drawing reactions
- Use integrated calculations in Marvin
- Graphical objects
- Import and export options
- Multipage documents
- Printing in MarvinSketch
- Chemical Features in MarvinSketch
- Marvin OLE User's Guide
- Appendix for MarvinSketch
- Tutorials
- Additional information
- MarvinSketch Developer's Guide
- MarvinSketch Application Options
- MarvinSketch Installation and Upgrade
- MarvinSketch Licensing
- MarvinSketch Getting Help and Support
- MarvinSketch Downloads
- MarvinSketch History of Changes
- MarvinView
- Introduction to MarvinView
- MarvinView Developer's Guide
- MarvinView Application Options
- MarvinView Installation and Upgrade
- MarvinView User's Guide
- MarvinView Getting started
- How to Use MarvinView Features
- MarvinView Graphical User Interface
- MarvinView Licensing
- MarvinView Getting Help and Support
- MarvinView Downloads
- MarvinView History of changes
- Molconvert
- Plexus Suite
- Quick Start Guide - Plexus Suite
- Plexus Suite User Guide
- Log in to Plexus Suite
- The Plexus Suite Dashboard
- Importing New Data
- Exporting Your Data
- Browsing in Your Data Set
- Selecting Data
- Searching in Your Database
- Saved Queries
- List Management
- Sorting Data
- Sharing Data with Other Users
- Calculating Molecular Properties for Single Compounds
- Adding calculated columns to tables
- Scaffold Based Enumeration
- Reaction Based Enumeration
- Registering Molecules in the Corporate Database
- ChemAxon Assay
- Charts view
- Plexus Suite Video Tutorials
- Plexus Suite Administrator Guide
- Plexus Connect Authentication
- Sharing Schema Items Among Users
- Business Flags
- Row-level Security
- Building blocks
- Admin Tools
- Adding JavaScript Files for Custom Functionality
- Writing JavaScript Files for Custom Functionality
- Integration with ChemAxon's Compound Registration System
- Shared data sources in Plexus Connect
- Configuration Files
- Edit Views
- Simple table
- Installation and System Requirements of Plexus Suite
- Plexus Suite Licensing
- Getting Help and Support for Plexus Suite
- Plexus Suite FAQ
- Plexus Suite Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use for the Plexus Suite Demo Site
- Plexus Suite History of Changes
- Schema Refresh Without Restart
- Zosimos
- Toolkits and Components
- AutoMapper
- Calculator Plugins
- Introduction to Calculator Plugins
- Calculator Plugins User's Guide
- Calculator Plugins Developer's Guide
- Background materials
- Calculation of partial charge distribution
- Generate3D
- Isoelectric point (pI) calculation
- LogP and logD calculations
- NMR model prediction
- pKa calculation
- Red and blue representation of pKa values
- Tautomerization and tautomers
- Validation results
- Tautomerization and tautomer models of ChemAxon
- Theory of aqueous solubility prediction
- The tautomerization models behind the JChem tautomer search
- Calculator Plugins Licensing
- Calculator Plugins FAQ
- Calculator Plugins Getting Help and Support
- Calculator Plugins History of Changes
- Calculator Plugins System Requirements
- Biomolecule Toolkit
- ChemAxon Synergy
- Document to Structure
- JChem Base
- JChem Base Administration
- JChem Base Developer's Guide
- JChem Base User's Guide
- Query Guide
- Search types
- Similarity search
- Query features JCB
- Stereochemistry JCB
- Special search types
- Search options
- Tautomer search - Vague bond search - sp-Hybridization
- Search Options Guide
- Atomproperty specific search options
- Attached data specific search options
- Bond specific search options
- Chemical terms specific search options
- Database specific search options
- General search options
- Hitdisplay specific search options
- Markush structure specific search options
- Performance specific search options
- Polymer specific search options
- Query feature specific search options
- Reaction specific search options
- Resultset specific search options
- Similarity specific search options
- Stereo specific search options
- Tautomer specific search options
- Standardization JCB
- Hit display-coloring
- Appendix JCB
- Matching Query - Target Examples
- jcsearch Command Line Tool
- jcunique Command Line Tool
- Homology Groups and Markush Structures
- Query Guide
- JChem Base FAQ
- JChem Base History of Changes
- JChem Base Getting Help and Support
- JChem Base Licensing
- JChem Choral
- JChem Neo4j Cartridge
- JChem Oracle Cartridge
- JChem Microservices
- JChem PostgreSQL Cartridge
- JChem Web Services Classic
- JKlustor
- Markush Tools
- Marvin JS
- Getting Started with Marvin JS
- Marvin JS Installation and System Requirements
- Marvin JS Developer's Guide
- Marvin JS User's Guide
- Editor Overview
- Editor Canvas
- Dialogs
- Abbreviated groups dialog
- Atom query properties dialog
- Attached Data dialog
- Bond properties dialog
- Export dialog
- Import dialog
- Periodic table dialog
- Atom properties dialog in Marvin JS
- Pseudo atom dialog
- Reaxys Group Generics dialog
- Repeating group dialog
- R-group dialog
- R-logic dialog
- Set box color dialog
- Text dialog
- View Settings dialog
- Toolbars
- Context menus
- Drawing and editing options
- Feature overview pages
- Keyboard Shortcuts in Marvin JS
- Editor Overview
- Marvin JS API Reference
- Online Examples
- Marvin JS Licensing
- Marvin JS History of Changes
- Marvin JS FAQ
- Marvin JS Getting Help and Support
- Marvin JS Video Tutorials
- Name to Structure
- Reactor
- Reactor User's Guide
- Introduction to Reactor
- Reactor Getting Started
- Reactor Concepts
- Reactor Examples
- Working with Reactor
- Specifying Reactions
- Specifying Reactants
- Reaction Mapping
- Reaction Rules
- Reactant Combinations
- Running Reactor
- Reactor Interfaces
- Reactor Application
- Reactor Command-line Application
- Reactor in Instant JChem
- Reactor in JChem for Excel
- Reactor in KNIME
- Reactor in Pipeline Pilot
- Reactor in Plexus Suite
- API, Web Services
- Glossary
- Reactor FAQ
- Reactor Licensing
- Reactor Getting Help and Support
- Reactor History of Changes
- Reactor Configuration Files
- Reactor User's Guide
- Screen
- Standardizer
- Standardizer User's Guide
- Standardizer Introduction
- Standardizer Getting Started
- Standardizer Concepts
- Working with Standardizer
- Standardizer Actions
- Add Explicit Hydrogens
- Alias to Atom
- Alias to Group
- Aromatize
- Clean 2D
- Clean 3D
- Clear Isotopes
- Clear Stereo
- Contract S-groups
- Convert Double Bonds
- Convert Pi-metal Bonds
- Convert to Enhanced Stereo
- Create Group
- Dearomatize
- Disconnect Metal Atoms
- Expand S-groups
- Expand Stoichiometry
- Map
- Map Reaction
- Mesomerize
- Neutralize
- Remove Absolute Stereo
- Remove Atom Values
- Remove Attached Data
- Remove Explicit Hydrogens
- Remove Fragment
- Remove R-group Definitions
- Remove Stereo Care Box
- Replace Atoms
- Set Absolute Stereo
- Set Hydrogen Isotope Symbol
- Strip Salts
- Tautomerize
- Transform
- Ungroup S-groups
- Unmap
- Wedge Clean
- Remove
- Standardizer Transform
- Custom Standardizer Actions
- Remove Solvents
- Creating a Configuration Standardizer
- Interfaces Standardizer
- Standardizer Actions
- Standardizer Developer's Guide
- Standardizer Installation and System Requirements
- Standardizer Licensing
- Standardizer Getting Help and Support
- Standardizer History of Changes
- Standardizer User's Guide
- Structure Checker
- Structure Checker User's Guide
- Introduction
- Structure Checker Getting Started
- Structure Checker Concepts
- Working with Structure Checker
- Checker List
- Abbreviated Group StrCh
- Absent Chiral Flag
- Absolute Stereo Configuration
- Alias
- Aromaticity Error
- Atom Map
- Atom Query Property
- Atom Value
- Atropisomer
- Attached Data StrCh
- Bond Angle
- Bond Length
- Brackets
- Chiral Flag
- Chiral Flag Error
- Circular R-group Reference
- Coordination System Error
- Covalent Counterion
- Crossed Double Bond
- Custom Checkers and Fixers
- Double Bond Stereo Error
- EZ Double Bond
- Empty Structure
- Explicit Hydrogen
- Explicit Lone Pairs
- Incorrect Tetrahedral Stereo
- Isotope
- Metallocene Error
- Missing Atom Map
- Missing R-group Reference
- Molecule Charge
- Multicenter
- Multicomponent
- Multiple Stereocenter
- Non-standard Wedge Scheme
- Non-stereo Wedge Bond
- OCR Error
- Overlapping Atoms
- Overlapping Bonds
- Pseudo Atom
- Query Atom
- Query Bond
- Racemate
- Radical
- Rare Element
- R-atom
- Reacting Center Bond Mark
- Reaction Map Error
- Relative Stereo
- R-group Attachment Error
- R-group Bridge Error
- R-group Reference Error
- Ring Strain Error
- Solvent
- Star Atom
- Stereo Care Box
- Stereo Inversion Retention Mark
- Straight Double Bond
- Substructure
- Three Dimension 3D
- Unbalanced Reaction
- Unused R-group Reference
- Valence Error
- Valence Property
- Wedge Error
- Wiggly Bond
- Wiggly Double Bond
- Creating a Configuration StrCh
- Interfaces StrCh
- Checker List
- Structure Checker Developer's Guide
- Structure Checker Installation and System Requirements
- Structure Checker Licensing
- Structure Checker Getting Help and Support
- Structure Checker History of Changes
- Structure Checker User's Guide
- Structure to Name
- Third-party Integration
- Cross Product Documentation
- ChemAxon Configuration Folder
- Chemical Fingerprints
- Chemical Terms
- File Formats
- Basic export options
- Compression and Encoding
- Document formats
- Graphics Formats
- Molecule file conversion with Molconverter
- Molecule Formats
- CML
- MDL MOL files
- Daylight SMILES related formats
- ChemAxon SMILES extensions
- IUPAC InChI, InChIKey, RInChI and RInChIKey
- Name
- Sequences - peptide, DNA, RNA
- FASTA file format
- Protein Data Bank (PDB) file format
- Tripos SYBYL MOL and MOL2 formats
- XYZ format
- Gaussian related file formats
- Markush DARC format - VMN
- CSV
- Input and Output System
- License Management
- Long Term Supported Releases - LTS
- Notice about CAS Registry Numbers®
- Other versions
- Public Repository
- Scientific Background
- Structure Representation
- Structure Representation - Class Representation
- Aromaticity
- Implicit, Explicit and Query Hydrogens
- Assigning stereochemistry descriptors
- Cleaning options
- Deprecated and Removed Methods
- Relative configuration of tetrahedral stereo centers
- Iterator Factory
- Atom and bond-set handling
- Graphic object handling
- Supported Java Versions
- Legal
- Discontinued Products
- Document to Database
- Fragmenter
- MarvinSpace
- MarvinSpace User's Guide
- MarvinSpace Developer's Guide
- MarvinSpace History of Changes
- Metabolizer
HTTP
This manual will give you a walk-through on how to use the HTTP web services.
Introduction
HTTP Service is the most lightweight and unrestricted remote service: it supports POST and GET requests to a predefined URL. Result is retrieved as is and rendered as a webpage.
Examples
Example #1
This example will show how to call chemicalize.com via an HTTP web service. In this case we want to calculate the pKa values of a molecule.
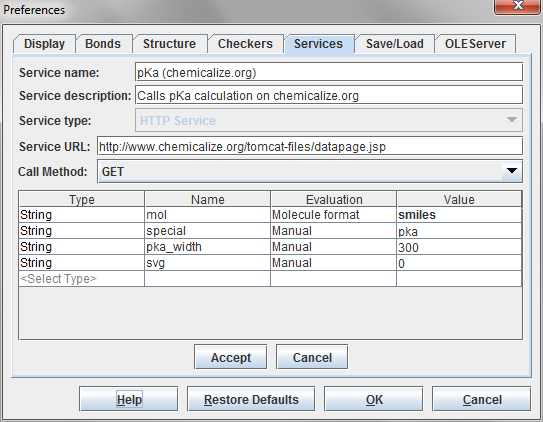
Fig. 1 HTTP service calling the pKa calculator of chemicalize.org
An example calculation with this webservice can be found below.
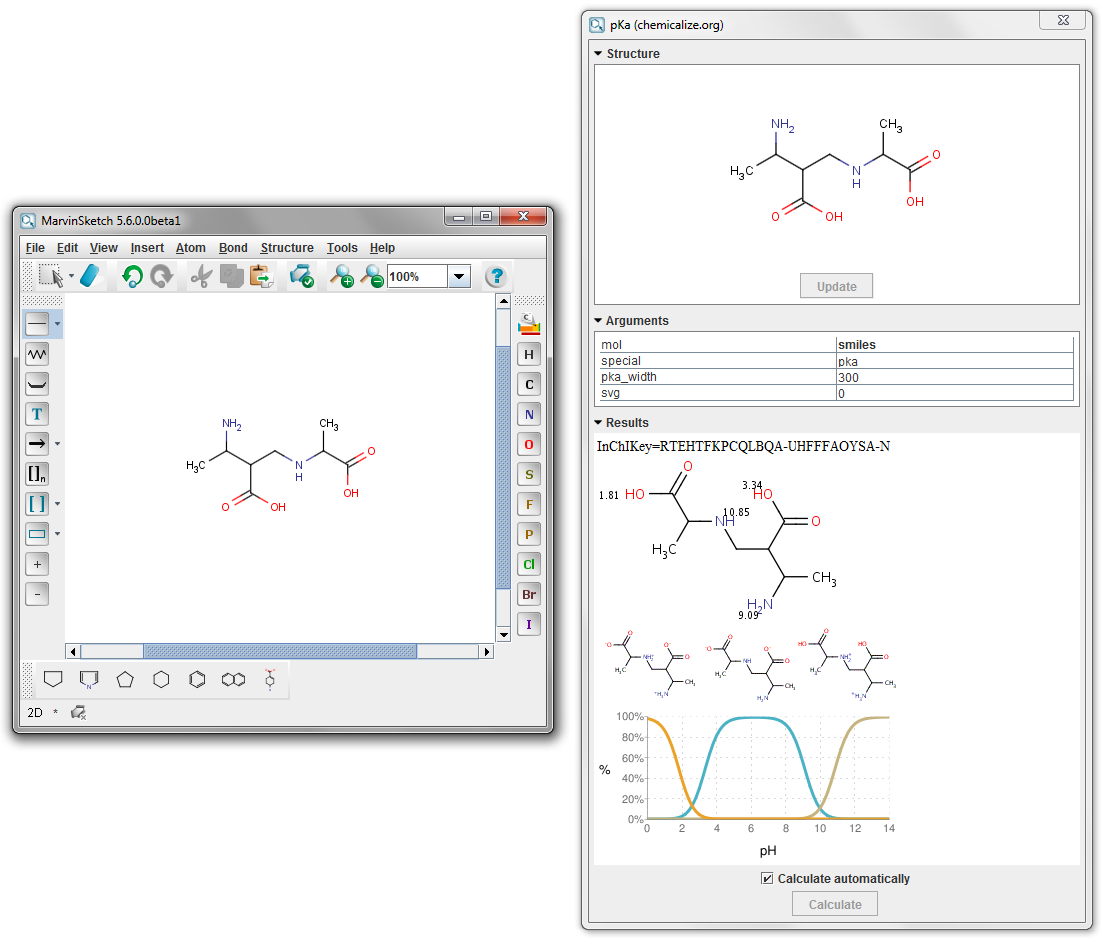
Fig. 2 Result of the pKa calculation via the webservice calling chemicalize.org
Example #2
This example shows how to reach the functionalities of chemicalize.com via HTTP API.
HTTPServiceDescriptor descriptor = new HTTPServiceDescriptor();
descriptor.setURL("https://chemicalize.com/tomcat-files/datapage.jsp");
descriptor.addArgument(ServiceArgument.createArgument("mol", ""));
descriptor.addArgument(ServiceArgument.createArgument("special", ""));
descriptor.addArgument(ServiceArgument.createArgument("pka_width", 0));
Object result = null;
try {
result = descriptor.getServiceHandler().callService(descriptor, "c1ccnccc1", "pka", 300);
} catch (ServiceException e) {
System.err.println("Service call failed.");
}
System.out.println("Synchronized call returned: " + String.valueOf(result));
descriptor.getServiceHandler().callService(descriptor, new AsyncCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result) {
System.out.println("Aynchronous call returned: " + result);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(ServiceException caught) {
System.err.println("Asynchronous call failed.");
}
}, "c1ccnccc1", "pka", 300);